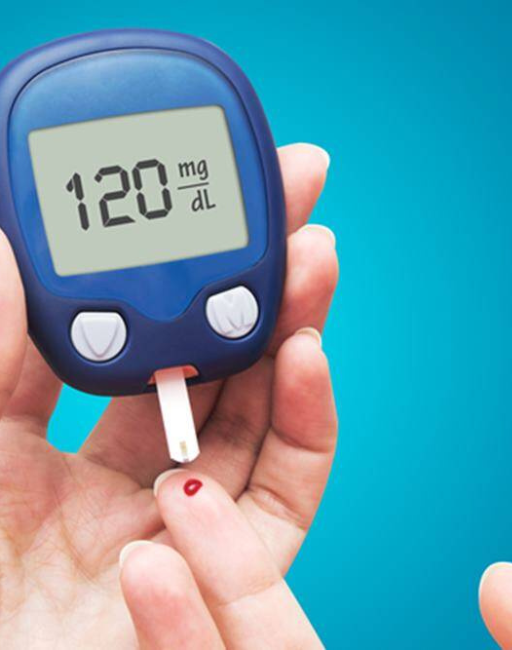
How is Diabetes Develops and manage ?
1. Development:
Type 1 Diabetes: The immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys insulin-producing cells in the pancreas.
Type 2 Diabetes: The body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn’t produce enough insulin, often due to lifestyle factors such as poor diet, lack of exercise, and obesity.
2. Management:
Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels: Regularly checking blood glucose levels to maintain them within a target range.
Medication: Taking insulin (for Type 1) or other medications (for Type 2) to control blood sugar levels.
Diet and Exercise: Eating a balanced diet and engaging in regular physical activity to help manage blood sugar levels.
Regular Check-Ups: Visiting healthcare professionals to monitor and manage any complications.